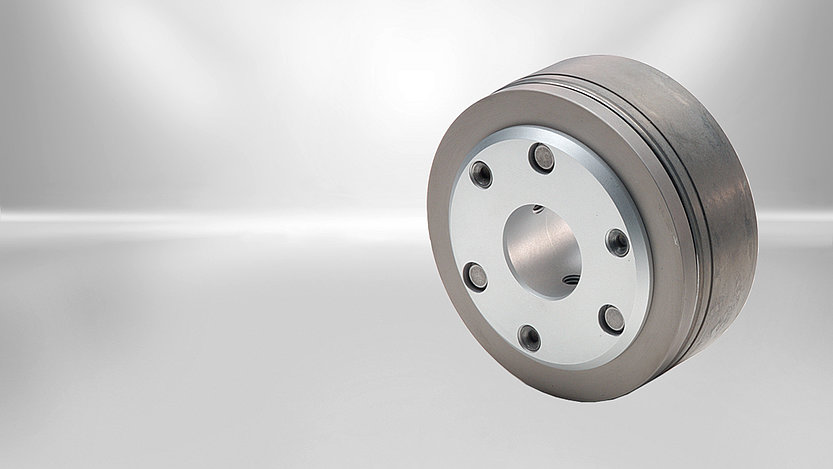
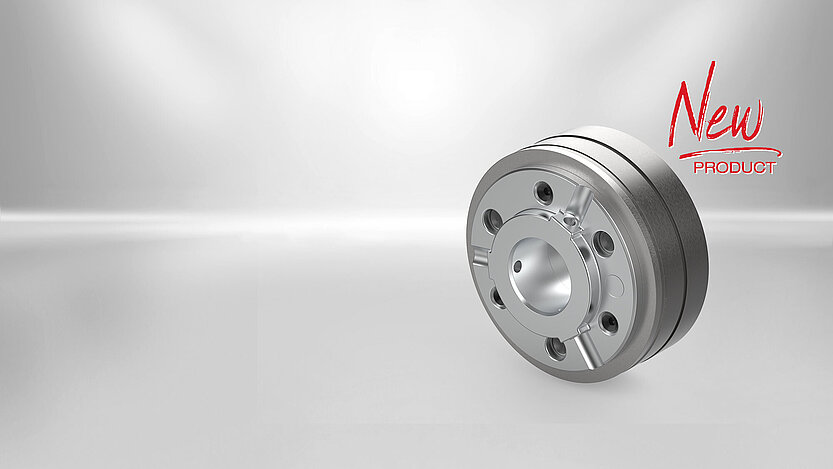
Our PM Line
Functionality
The PM Line includes permanent magnet brakes in which the braking force is generated by a permanent magnetic field. The brake thus works in a de-energized condition and fulfils the following functions: Holding, positioning and emergency stop. The neutralization of the braking force is effected by the counteracting electric field, granting a high degree of security, even in the case of power failure. Permanent magnet brakes are characterized by a secure, residual-moment-free lifting in any position, and by a backlash-free transfer of the braking torque.
Operating principle
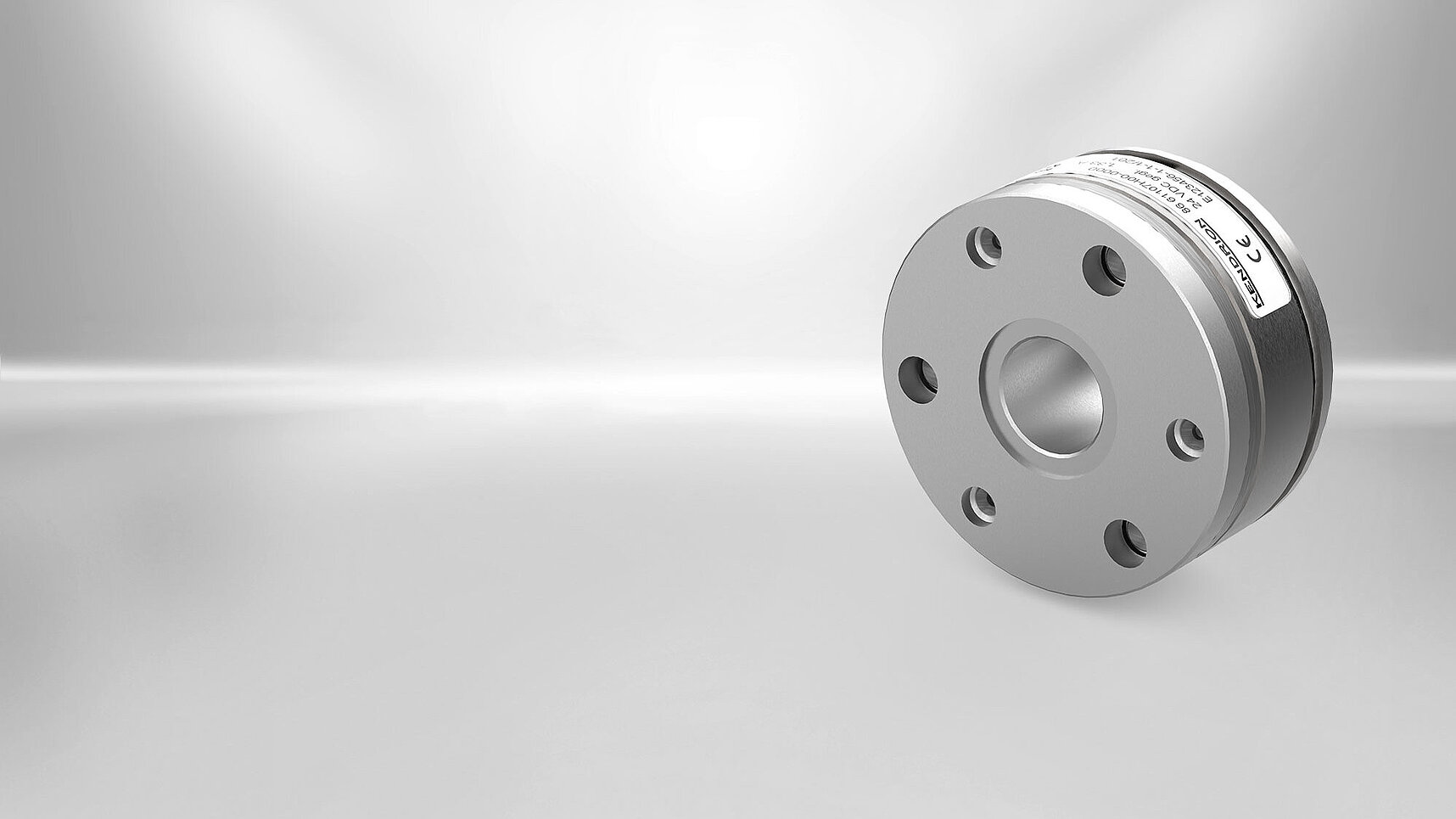
The permanent-magnet single-surface brake is designed to operate dry. The force generated by a permanent magnetic field is utilised to produce the braking effect. To neutralise the braking action, the magnetic flux of the permanent magnets is cancelled by an alternate electromagnetic field (electromagnetically released system). The zero backlash connection between the armature and flange hub ensures zero backlash transmission of the brake torque to the machine shaft (e.g. motor shaft) and reliable release of the permanent-magnet single-surface brake with zero residual torque. Thanks to these features, permanent-magnet single-surface brakes are ideal for servo motor applications.
Brake design
The firmly fitted field coil is installed between the outer ring and inner ring of the permanent-magnet single-surface brake. The flying leads required to connect the field coil exit on the brake circumference. The permanent magnets installed in axial direction between the outer ring and the flange of the inner ring generate the magnetic field required to produce the braking action. The armature is connected with the flange hub by means of segmental springs and rivet fasteners to establish an axially movable, torsion-proof and friction-free connection. This ensures zero residual torque during horizontal or vertical brake operation. The rated air gap 's' between the armature and outer ring of the permanent-magnet single-surface brake is adjusted during brake mounting (e.g. through mounting tolerances). The flange hub is attached to the machine shaft (e.g. motor shaft) in such a way that a torsion-proof and axially fixed connection is achieved. The permanent magnetic field attracts and pulls the armature in frictional contact with the outer ring or inner ring to generate the brake action. When DC voltage is applied to the field coil of the permanent-magnet single-surface brake, the alternate electromagnetic field offsets the force exerted on the armature by the permanent magnetic field and the brake is released. Except for the minimal force exerted by the segmental springs, the shaft to be braked is not exposed to any other axial force.

Visit our Kendrion ProductFinder
Find technical data and product-specific information about our brake portfolio in our ProductFinder!
To the product FINDER for BRAKES