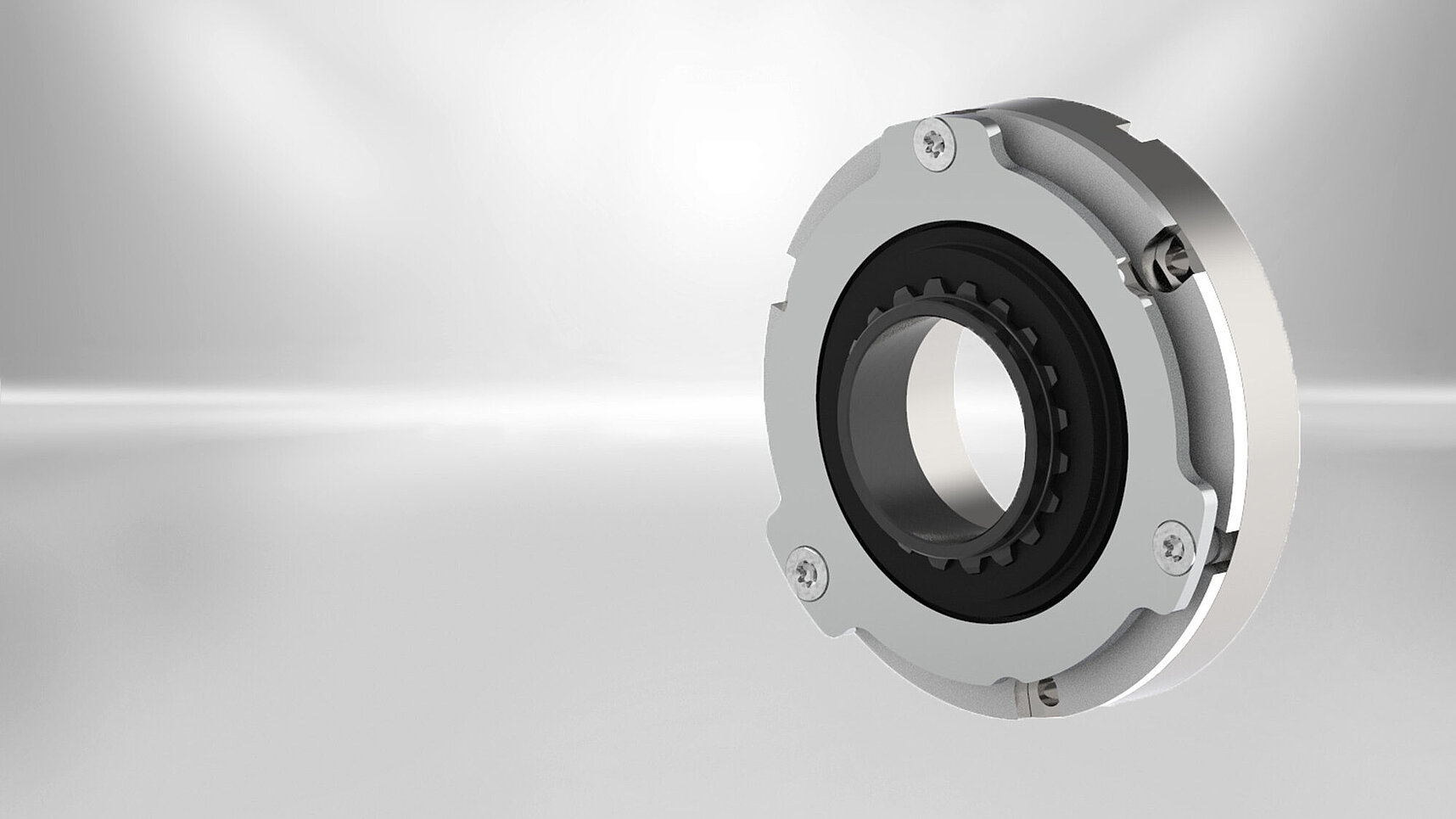
Our Servo Slim Line
The new Servo Slim Line solution is based on the spring pressure principle and is suitable for industrial robots with high braking energy and long required service life
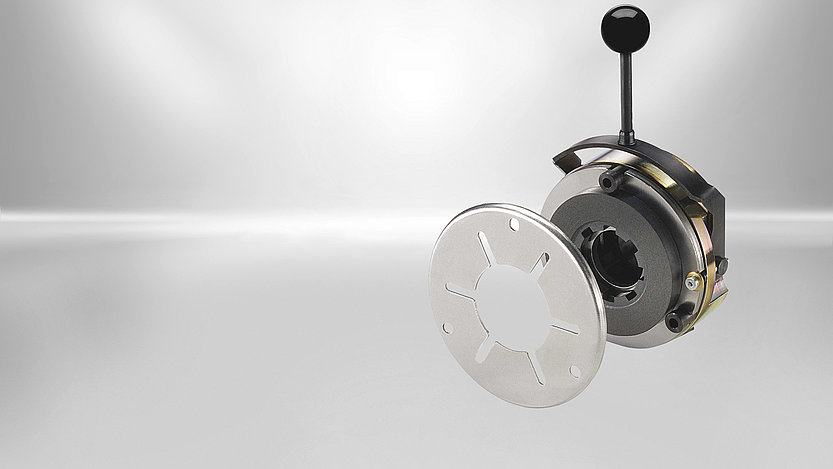
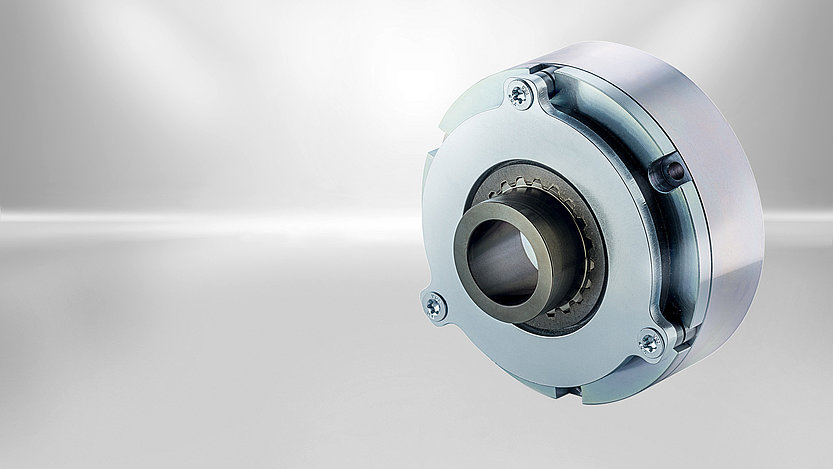
The spring-applied brakes which are ideally suited for robotics is designed for robotics solutions and loads of up to appr. 20 kg, but it can also be used in other applications requiring small geometrical dimensions. With regard to their power density the slim single-disc brakes are flatter and lighter than the market standard, and due to their large inner diameter they are well suited for hollow-shaft drives. This makes them perfect for applications in lightweight robots with integrated drives.
The optimal solution for robotics
There is a growing demand for safety technology in order to avoid injuries by collisions, especially if the control technology or even the power supply fails. In this case electromagnetic brakes are usually the method of choice. As safety brakes they bring moving masses to a stop, keep loads in position and therefore prevent humans and material assets from being affected.
For decades Kendrion has been supplying brakes for industrial robots with loads higher than 20 kg. In order to be able to serve the booming market of smaller robots the brake specialist has invested a lot into the research and development of suitable brakes for robotics applications in recent years. With many years of experience and the latest findings from the market ideally suited solutions for robotics have been developed.
Manufacturing technology
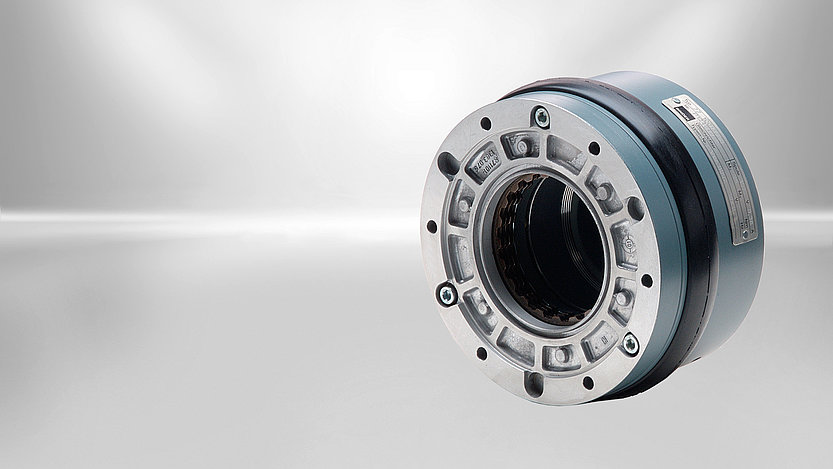
A patented manufacturing technology provides the basis for this solution: In case of conventional spring-applied brakes the production-related tolerances of the air gap, i.e. the distance between friction disc and armature plate, must be taken into account. When designing the brake for the worst case the maximum rated air gap is considered. Both lifetime and torque are directly related to the so-called maximum operating air gap which results from the maximum rated air gap and the wear. Thus, it is essential to keep the rated air gap as narrow as possible. With conventional manufacturing technologies rated air gap tolerances between one and two tenths of a millimetre can be achieved. With the proven solution from Kendrion rated air gap tolerances of about four hundredths of a millimetre are standard. The potential saved is used to increase the holding torque or extend the lifetime, thus increasing the power density of the brake.
Expertise from the laboratory
When it comes to validation and verification of the values the user can rely on the competent lab team of the brake specialist. Over the years, Kendrion has developed great competence in testing and qualifying its products. The lab is equipped with test devices for the measuring range from 0.1 Nm to 10,000 Nm. The test setups reflect application conditions 1:1 and can so reproduce real circumstances. All measurement data are recorded under different operating conditions such as temperature, friction work, rotational speed and direction of rotation and are gathered for the technical data. Due to these options the user can be provided with well-founded technical details.
Technical Details
| Size | 03 | 04 | 05 | 07 | 09 | 10 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min. transmitted torque M4min [Nm] | 0.27 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 1.7 | 4.0 | 5.0 | 11 |
| Nominal power PN [W] | 5.8 | 8.3 | 10.3 | 11.4 | 14 | 20 | 27.2 |
| Standard rated voltage UN [VDC] | 12 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 |
| Ambient temperature | -10 bis 100 | -10 bis 100 | -10 bis 100 | -10 bis 100 | -10 bis 100 | -10 bis 100 | -10 bis 100 |
| Number of emergency stops Zges mit W1max | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| Nominal speed nn [min-1] | 6000 | 6000 | 5000 | 4000 | 3000 | 3000 | 2500 |
| Outside diameter D1 [mm] | 32 | 38 | 51 | 69 | 86 | 105 | 127 |
| Inner diameter D2 [mm] | 9 | 11.5 | 22 | 30 | 43 | 58 | 63 |
| Lenght L1 [mm] | 16 | 16 | 16 | 18 | 21 | 21 | 29.3 |